Every year, millions of car accidents occur globally, making knowledge of first aid an essential skill for drivers and passengers alike. The initial moments following an accident are crucial in determining the outcomes for those involved. Understanding and effectively applying first-aid can significantly alter the impact of these incidents.
Immediate Response After a Car Accident
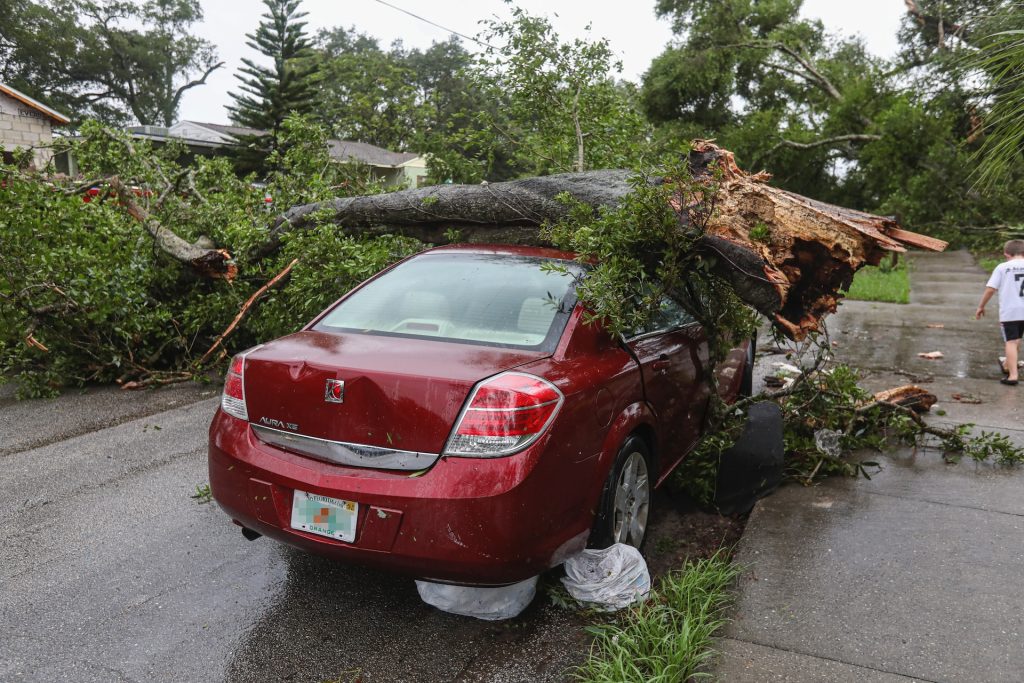

1. Ensuring Personal Safety
The chaos following a car accident can be overwhelming. The first step is to ensure your safety. If you are uninjured and it’s safe, exit the vehicle and move to a secure location. Avoid standing on the road or in an area where secondary accidents could occur. Your ability to assist others hinges on your safety, so assess your condition first.
2. Assessing the Situation
Once safe, quickly gauge the severity of the accident. Look for hazards like fire, leaking fuel, or traffic. Count the number of vehicles involved and check if anyone is in immediate danger or needs urgent help. This assessment is crucial for providing accurate information to emergency responders.
3. Calling for Help
Immediately call emergency services. Be precise about your location, using road signs or GPS if available. Describe the nature of the accident, the number of vehicles involved, and any visible severe injuries. Speak clearly and calmly. The information you provide is vital for the dispatch of appropriate resources.
4. Assisting the Injured
Approach the injured cautiously. If you’re not trained in first aid, avoid moving them, as this could exacerbate their injuries. If they are conscious, ask simple questions to gauge their awareness and look for visible injuries. In case of unconsciousness, check for breathing and pulse. If trained, administer necessary first aid or CPR.
5. Handling Specific Scenarios
If someone is unconscious, assess their responsiveness by gently tapping them and shouting. If they don’t respond and you’re trained, begin CPR. In cases where individuals are trapped, avoid moving them unless there’s an immediate risk, like fire. With burns, remove the source of the burn if safe to do so, and cool the area with lukewarm water. Avoid applying ice, which can further damage the skin.
6. Psychological First Aid
Psychological first aid involves providing emotional and psychological support. Speak in a calm, reassuring voice. Let victims know help is on the way. Listen to them without forcing conversation. Managing panic can prevent shock and further trauma.
7. Preparation and Prevention
Maintaining a well-equipped first-aid kit in your car is essential. Basic items should include various sizes of bandages, antiseptic wipes, sterile gauze, adhesive tape, scissors, disposable gloves, a thermal blanket, and a basic first-aid manual. Regularly check and replenish your kit. Alongside the kit, consider enrolling in a first-aid course. Being prepared can significantly affect the outcome of a road accident.
list of items you should consider including in your car’s first aid kit
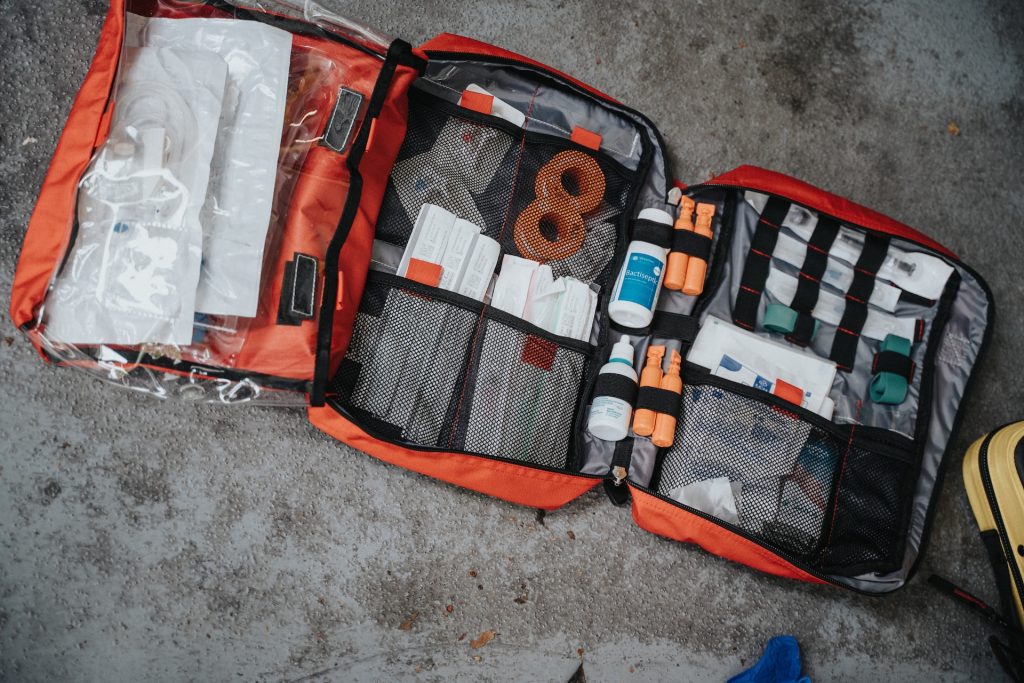

- Sterile Gauze Pads and Rolls: For dressing wounds and controlling bleeding.
- Adhesive Bandages (Various Sizes): For covering small cuts, blisters, or abrasions.
- Antiseptic Wipes or Solution: To clean wounds and prevent infection.
- Adhesive Tape: To secure gauze or bandages.
- Elastic Bandages: For wrapping sprained or strained joints.
- Triangular Bandages: Useful for creating slings or wrapping injuries.
- Antibiotic Ointment: Apply on small wounds to prevent infection.
- Pain Relievers: Such as aspirin, ibuprofen, or acetaminophen.
- CPR Mouth Barrier: For performing CPR safely.
- Disposable Gloves: To protect yourself and the injured person from infection.
- Thermal Blanket: For retaining body heat in cases of shock or exposure.
- Tweezers: For removing splinters or debris from wounds.
- Scissors: For cutting tape, clothing, or bandages.
- Instant Cold Packs: For reducing swelling and numbing pain.
- Eye Wash Solution: To flush out irritants from the eyes.
- Burn Gel or Cream: For minor burns.
- Emergency Contact Information: Including numbers for family members, doctors, local emergency services, and roadside assistance.
- First-Aid Manual: A basic guide to handling common injuries.
- Allergy Medications: Like antihistamines for unexpected allergic reactions.
- Breathing Barrier Mask: For safe mouth-to-mouth resuscitation.
- Flashlight and Extra Batteries: For visibility in case of accidents at night.
- Safety Pins: For securing bandages or clothing.
First-Aid Tips for Common Injuries
- Head Injuries: Head injuries can be deceptive. A person may be conscious but disoriented, which can indicate a serious injury. If there’s bleeding, apply gentle pressure with a clean cloth. Avoid moving the person unless necessary, and continually monitor their consciousness and breathing.
- Bleeding: Severe bleeding requires immediate attention. Apply direct pressure to the wound with a clean cloth or bandage. If the bleeding doesn’t stop, maintain pressure and elevate the injured area if possible. Avoid using tourniquets unless you are trained to do so.
- Fractures: Immobilizing the injured area is key. Use makeshift splints only if you must move the person. Avoid trying to correct the position of the bone. Cover open fractures with clean materials and avoid applying pressure directly on the bone protrusion.
- Shock: Symptoms of shock include pale, cold, clammy skin, rapid breathing, and a weak pulse. Lay the person down, elevate their feet about 12 inches, and cover them with a blanket. Do not give them anything to eat or drink.
Conclusion
While we all hope never to be in a car accident, being prepared with first-aid knowledge is crucial. Remember, safety comes first, followed by calling for help, providing care, and offering support. Your actions can significantly impact the well-being of those involved in a car accident. Stay informed, stay prepared, and you could be a lifesaver in a critical situation.